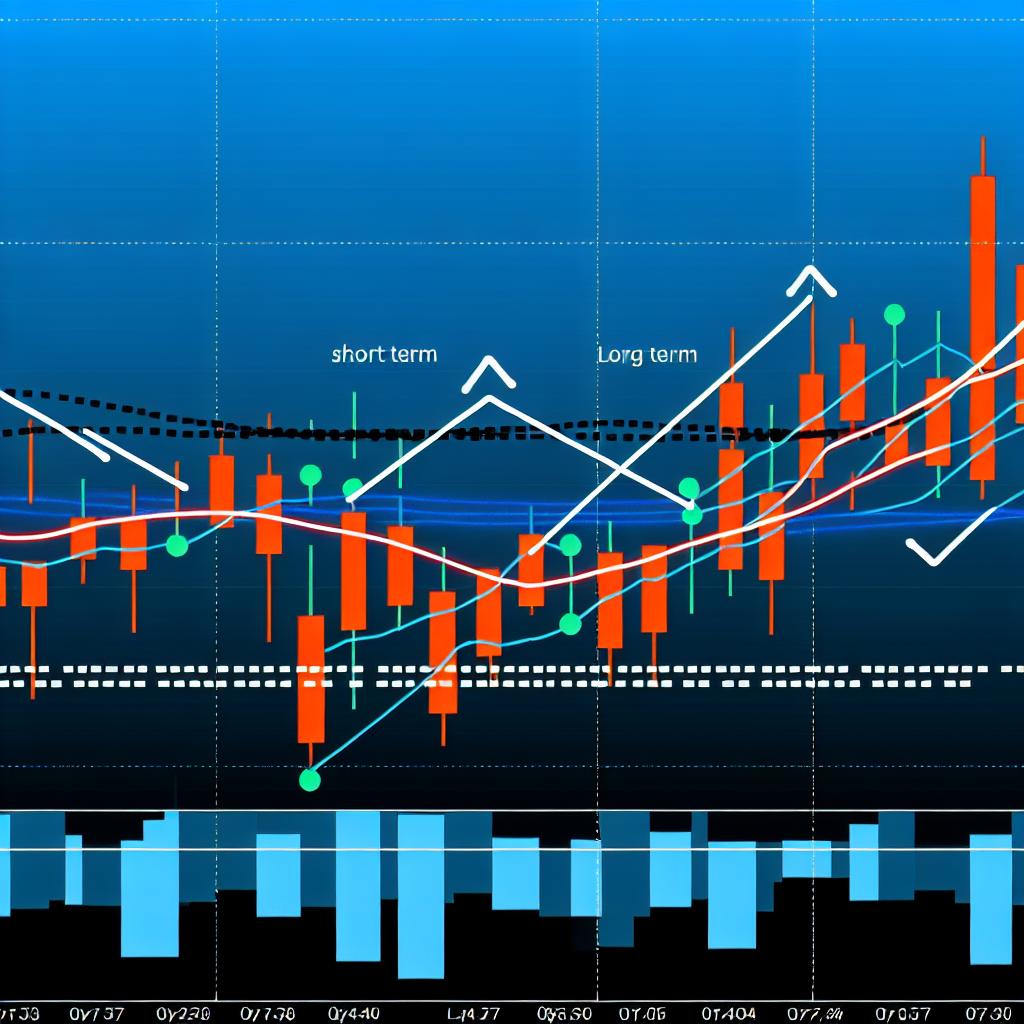
Understanding the Moving Average Crossover Strategy
The Moving Average Crossover Strategy is widely recognized among traders, especially those involved with binary options. The fundamental idea of this strategy is to utilize the interaction between two distinct moving averages—typically one being a short-term average, while the other is a long-term average. This interaction helps traders identify potential buy or sell signals. To effectively apply this strategy, it is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of its mechanics and components.
Components of the Strategy
1. Moving Averages: Essentially, a moving average is a statistical calculation intended to analyze a series of data points by developing a series of averages from various subsets of the complete dataset. The primary function of a moving average is to smooth price data, making it easier to ascertain the prevailing direction of a trend. By filtering out the noise from random short-term price fluctuations, moving averages provide a more stable line that precisely depicts the underlying trend.
2. Types of Moving Averages: There are primarily two types of moving averages crucial to understanding this strategy:
- Simple Moving Average (SMA): This is the most straightforward form of moving average and is calculated by adding up the most recent prices over a specific period and dividing the sum by the number of time periods. Despite its simplicity, the SMA is a popular choice for many traders looking to implement the crossover strategy.
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA): Unlike the SMA, the EMA gives more weight to the most recent data points. This weighted approach makes the EMA more responsive to changes and updates in price, causing it to react faster to market movements. Traders often prefer the EMA when they seek to capture currency trends at the earliest possible stage.
Identifying Crossovers
The primary application of the moving average crossover strategy is in identifying potential shifts or turning points within the market. These turning points are signaled by two main types of crossovers:
Golden Cross: This bullish signal occurs when the short-term moving average crosses above the long-term moving average. It indicates a potential upward trend, and many traders use this signal as a prompt to buy. The golden cross is a particularly powerful signal in the context of long-term bullish markets and is seen by many as a strong indicator of potential upward momentum.
Death Cross: Conversely, this bearish signal is identified when the short-term moving average crosses below the long-term moving average. It often suggests a potential downward trend, leading traders to interpret it as a sell signal. The death cross is often associated with imminent bearish market trends, especially when observed on longer timeframes.
Implementing the Strategy in Binary Options
Binary options trading provides a framework for traders to make predictions about price movements with defined risk and reward conditions. Proper implementation of the moving average crossover strategy in this domain involves several critical considerations:
1. Time Frame Selection: Choosing the correct time frame is vital and should correspond with your trading style and objectives. Short-term charts, such as 15-minute or 30-minute charts, might offer more frequent signals, but they also contain more market noise. On the other hand, longer-term charts such as daily or weekly provide fewer signals but usually have higher reliability.
2. Expiry Times: The selection of an appropriate expiry time is crucial and should match the time frame used in identifying the crossover signal. For example, when working with a 15-minute chart, an expiry that aligns closely with this timeframe may furnish a better outcome.
3. Market Conditions: Traders must also assess the prevailing market conditions to see if they are conducive to employing the crossover strategy. Generally, trending markets tend to produce clearer and more decisive signals, while ranging or flat markets can generate numerous false indications.
Limitations and Considerations
While the moving average crossover strategy has its uses, there are several limitations and considerations to keep in mind:
1. False Signals: In many scenarios, moving averages can produce false signals in choppy or range-bound markets, leading to misguided trades. Thus, it is essential to integrate other forms of analysis, such as assessing support and resistance levels, to confirm signals generated by moving averages.
2. Lagging Nature: By their nature, moving averages are lagging indicators, reflecting past price action. This inherent characteristic can result in delayed entry or exit points, especially in fast-moving markets.
3. No Guarantee of Success: As is the case with any trading strategy, the moving average crossover strategy does not guarantee successful outcomes. Therefore, prudent risk management practices must be employed and trades should not rely solely on crossover indicators without considering the broader market context.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Moving Average Crossover Strategy represents a potentially powerful tool for those engaged in binary options trading who are looking to capitalize on market trends. By gaining a solid grasp on moving averages, recognizing key crossover points, and taking into account market conditions, traders can better refine their decision-making process. Nevertheless, it is imperative to maintain an awareness of the inherent limitations inherent in the strategy and incorporate other analytical tools for comprehensive market analysis. For those interested in expanding their knowledge or exploring advanced techniques, engaging with resources from trading platforms could provide valuable insights into optimizing trading strategies.
This article was last updated on: May 18, 2025