Bollinger Bands Overview
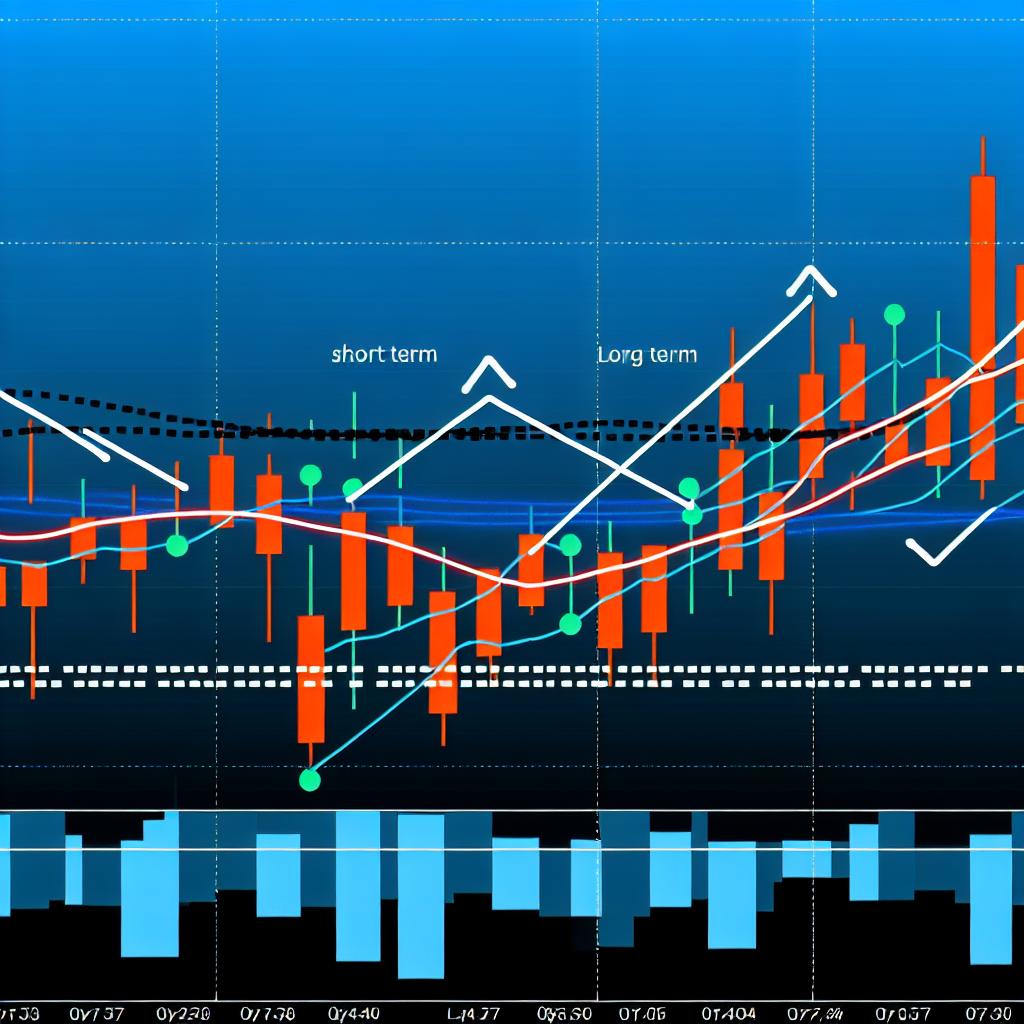
Bollinger Bands are a widely-used technical analysis tool developed by financial analyst John Bollinger in the early 1980s. These bands are instrumental in measuring market volatility and identifying possible market reversals, making them a valuable asset for traders and analysts. The tool comprises three lines: a middle band, which is generated using a simple moving average (SMA), flanked by two outer bands that denote standard deviations away from the SMA. The positioning of these bands changes in relation to market volatility, expanding during periods of high volatility and contracting as volatility subsides.
How Bollinger Bands Work
The foundational middle band is usually set as a 20-day SMA, although this default setting can be adjusted to align with a trader’s specific strategy or time-frame. The upper and lower bands typically lie 2 standard deviations away from the SMA, which is a setting that captures approximately 95% of price movements. This characteristic makes Bollinger Bands a dependable tool for traders seeking to spot changes in market volatility dynamically.
Spotting Market Reversals
A principal advantage of Bollinger Bands lies in their ability to signal potential market reversals. When prices breach the bands, it typically signifies a significant increase in volatility, a cue that traders often interpret as a potential market turning point. Here’s how these indicators work:
1. Overbought and Oversold Conditions: When the market price contacts or surpasses the upper band, it may signal an overbought market condition, whereas a descent below the lower band might suggest an oversold market. These situations are frequently precursors to market reversals, indicating new opportunities for traders.
2. Bollinger Squeeze: The term “squeeze” refers to a scenario where the bands constrict, indicative of low volatility. This contraction usually precedes a period of increased volatility, signaling a potential breakout in price that often marks a market reversal.
Combining Bollinger Bands with Other Indicators
While Bollinger Bands offer crucial insights on their own, they are commonly used in combination with other technical indicators to increase the robustness and reliability of market predictions:
1. Relative Strength Index (RSI): When traders use Bollinger Bands alongside the RSI, a momentum oscillator, it offers a more nuanced perspective, aiding in the confirmation of overbought or oversold market conditions. This consolidated approach provides a more reliable indicator of potential market reversals by reinforcing signals given by Bollinger Bands.
2. Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD): Using the MACD indicator with Bollinger Bands helps detect trends and shifts in market momentum. When these indicators align, they provide a clearer, comprehensive view of market sentiment, making them powerful tools for traders looking to capitalize on market trends.
Practical Application and Considerations
While Bollinger Bands are effective in recognizing market reversals, they should ideally be part of a broader, well-rounded trading strategy. Traders must take into account various other factors including current market conditions, trading volumes, and fundamental analysis. Furthermore, the default settings of the Bollinger Bands might require adjustments to better suit individual trading styles or market specifics.
Traders looking for comprehensive technical analysis strategies may benefit from exploring resources provided by professional trading platforms or educational websites within the trading community, such as Investopedia.
Understanding the effective application of Bollinger Bands, in tandem with complementary technical indicators, enhances a trader’s ability to accurately identify and act upon market reversals. This multidimensional approach equips traders to seize opportunities in the marketplace with greater confidence and precision. By recognizing the strengths and limitations of Bollinger Bands and combining them with other analytical tools, traders can refine their strategies and improve their trading outcomes significantly.
In-Depth Analysis of Bollinger Bands’ Components
To fully comprehend the utility of Bollinger Bands, it is crucial to investigate each element that constitutes this technical tool. The three bands play distinct roles in elucidating market conditions:
The Middle Band: The Simple Moving Average (SMA)
The middle band acts as a baseline within the structure of Bollinger Bands. The SMA, typically calculated over a 20-day period, averages the sum of closing prices over a predetermined time frame. It serves as a reference point for identifying trends, allowing traders to gauge the market’s average position over that period and configure their strategies accordingly.
Upper and Lower Bands: Standard Deviations from the SMA
The outer bands, often standard deviations away from the SMA, signify the boundaries of expected price movements. Their primary function is to encapsulate most of the price action, with the standard setting at 2 standard deviations effectively enveloping approximately 95% of market movements. This statistical approach provides traders with a probabilistic estimate of price fluctuations, facilitating better-informed trading decisions.
Strategic Use in Different Market Conditions
Bollinger Bands adapt to various market scenarios, offering insights into trends, breakouts, and reversals. Understanding how to deploy them effectively under differing market conditions can enhance their utility:
Trending Markets
In trending markets, the price tends to ride along the outer band. In an uptrend, prices may consistently meet or exceed the upper band, while in a downtrend, they often touch or go below the lower band. Using Bollinger Bands alongside trend indicators allows traders to confirm these trends and strategically position their trades.
Range-Bound Markets
In conditions where markets are trading within a range, Bollinger Bands can help identify potential breakouts. As the price oscillates between support and resistance, Bollinger Bands highlight where momentum might shift, helping to preempt and capitalize on potential price movements.
Advanced Bollinger Bands Techniques
Traders who seek to harness the full potential of Bollinger Bands might consider incorporating advanced techniques into their analyses:
Multiple Time Frame Analysis
Employing Bollinger Bands across different time frames can provide a more comprehensive view of market dynamics. Observing how Bollinger Bands behave on a shorter time frame while consulting a larger time frame can yield insights into the intensity and longevity of a trend or reversal.
Bollinger Band Width
The Bollinger Band Width is an auxiliary indicator derived from the difference between the upper and lower bands. Its fluctuations offer clues about forthcoming periods of volatility, with narrower widths suggesting potential breakouts. Traders may use this indicator to anticipate significant market movements or refine entry and exit points.
Limitations and Considerations
While Bollinger Bands are a potent tool, they are not infallible. Traders must recognize their limitations and employ them as part of a broader analytical strategy:
False Breakouts
False breakouts can occur, where prices momentarily breach the bands before reverting. Traders should be wary of these instances, which mand
ate confirmation through other indicators or tools to mitigate erroneous trades.
Customization Needs
The default settings of Bollinger Bands might not fit all market scenarios or assets. Customizing the period of the SMA or adjusting the standard deviation settings can improve their applicability to specific trading strategies or asset classes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Bollinger Bands provide valuable insights into market volatility and potential reversals, serving as a crucial component of many traders’ technical analysis toolkits. While powerful on their own, their utility is often enhanced when used alongside other indicators and within a broader, well-considered trading strategy. By understanding their application and limitations, traders can employ Bollinger Bands to make more informed, strategic decisions in the dynamic world of trading.